Difference between revisions of "Single cylinder engine"
m |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
{{Piston engine configurations}} | {{Piston engine configurations}} | ||
| + | {{Machine configurations|state=uncollapsed}} | ||
| + | |||
[[Category: Engine technology]] | [[Category: Engine technology]] | ||
Revision as of 12:23, 15 July 2008
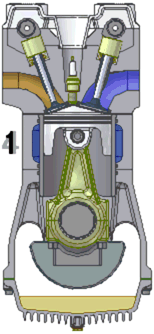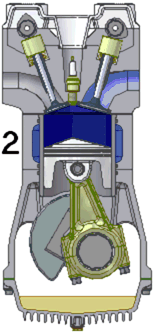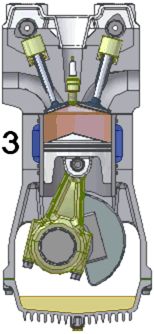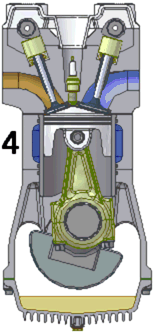
A single cylinder engine, colloquially known as a one-lunger, is an engine configuration consisting of just one cylinder, the simplest arrangement possible for an Otto or Diesel engine. The mounting can be standing, lying or angled..
Pros and Cons
Compared to multi-cylinder engines, single cylinder engines have several advantages, primarily their simple and economical construction. Balance shafts and counterweights on the crankshaft must be used to balance the weight of reciprocating parts, and can be expensive and complicated due to the collective mass of multiple cylinders. The biggest downside of the single cylinder engine is that it develops considerably lower power to weight ratios than a multi-cylinder of the same type.
Uses
Some early automobiles, such as the Cadillac 1906 Model K and 1907 Models L and M used single-cylinder engines [1]. Single cylinder engines were also popular at one time for marine uses (see external links, below). Today the most common configuration is the 50cc-two-stroke Otto seen in so many bikes and scooters. These vehicles allowed the first mass-motorisation in many countries. Most engines used in small portable appliances, such as chainsaws, generators and domestic lawn mowers, usually have one cylinder. Also, the one-lunger is used in working vehicles, motorsports, airplanes, and as an industrial motor.
External links
- european supermono series
- Preston Services (Kent, UK) website, containing images of several single-cylinder marine engines for sale.
- Old Marine Engines
- Old Marine Engine Discussion Board
| Piston engine configurations | |
|---|---|
| Straight | Single, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14 |
| V | 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24 |
| Flat | 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, H |
| W | 8, 9, 12, 16, 18 |
| Other inline | H, VR, Opposed, U (Square), X |
| Other | Hemi, Radial, Rotary, Pistonless, Deltic, (Wankel) |
| Heat engines | |
|---|---|
| Stroke cycles One • Two • Four • Six • | |
| Engine types Gas turbine • Piston • Jet • Rocket engine • Steam engine • Stirling engine • Tschudi• Twingle Rotary • Wankel • Free-piston • Britalus • Coomber • Swing-piston • Orbital • Quasiturbine | |
| Valves Cylinder head porting • D slide • Four-stroke • Manifold • Multi • Piston • Poppet • Sleeve | |
| Piston layouts Single cylinder • Straight • Opposed • Flat • V • W • H • Deltic • Radial • Rocket engine nozzle • Rotary • Stelzer • Controlled Combustion • Bourke | |
| Motion mechanisms Cam • Connecting rod • Coomber rotary • Crank • Crank substitute • Crankshaft • Linkages (Evans • Peaucellier-Lipkin • Sector straight-line • Watt) • Double acting/differential cylinder | |
| Thermodynamic cycle |
